I watched High Fidelity [IMDB, Wikipedia] for the first time over the weekend. It’s okay. It’s pretty clear that anyone that liked Empire Records [IMDB, Wikipedia] when they were 20 years old would love High Fidelity when they’re 25.
Mikhail Bulgakov: The Master and Margarita
On the advice of a friend, I’ve started another step in my meandering through the Russian classics. In particular, I have started to read Mikahil Bulgakov‘s The Master and Margarita.
I picked up the 2007 Penguin Classics version (ISBN978-0-140-45546-5) from the ever-fantastic Foyles (I swear, Foyles alone is reason enough to live in London). It has a helpful cronology of major events in Russian history from the Russo-Turkish war (1871-8) to Nazi Germany’s invasion of the U.S.S.R. (1941), and a series of notes on obscure references throughout the text.
I’m only two chapters in, so far, but it already seems fantastic.
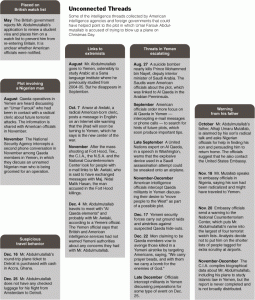
Clues they missed
The NY Times has a nice piece summarising the clues that were not put together prior to the attempted Christmas Day attack on the Northwestern flight to Detroit. All of those clues are presented in this graphic:
The article speaks of poorly designed computer systems, phrases mentioned in speeches (which, frankly, would be incredibly difficult to automatically include in your analysis) and general stories of the left hand not knowing what the right hand is doing within the US intelligence community. To my mind, though, it really comes down to just a few simple points:
- His own father had contacted the US to say that his son was missing and possibly being “radicalised,” leading to his being placed on a watch list.
- He bought the ticket with cash.
- He checked no luggage.
I firmly believe that most airport security is theatre, but the combination of just those three points should surely have warranted an individual pat-down.
Wanted: A measure of semantic correlation
“The quick, brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.” and “There is a dog and a fox. The fox, which is brown, jumps over the dog, which is lazy. The fox is quick.” should give a value of 1.
“The quick, brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.” and “There is a dog and a fox. The fox, which is brown, jumps over the dog, which is lazy. The fox is fast.” should give a value of 0.999.
Yes, I know that it’s complicated; but it’s not impossible. Google clearly does something similar when grouping stories together for news.google.com.
Then I want to have all news stories automatically compared to corporate press releases. I want my webpage to show me the press release on one side and the news article on the other. I want the news article to be shaded with two different colours; one colour for sections that are possibly reworded, but ultimately just taken from the press release and one colour for sections that represent actual work done by the reporter.
W4nkr
Taken at 12:13pm, Monday the 18th of January, 2010, on Russell Square (where Woburn Place turns into Southampton Row).
Auto-appendectomy: the removal of one’s own appendix
Those crazy Russians! In 1961, a team of 12 Russians spent the winter in Antarctica. The doctor, a surgeon, developed appendicitis and eventually cut out his own appendix.
The story is in the 15 December 2009 edition of the British Medical Journal.
The skill at writing that the guy possessed is incredible. Look at this, written in his journal while suffering appendicitis:
“I did not sleep at all last night. It hurts like the devil! A snowstorm whipping through my soul, wailing like a hundred jackals. Still no obvious symptoms that perforation is imminent, but an oppressive feeling of foreboding hangs over me.”
Here he describes the operation:
“I didn’t permit myself to think about anything other than the task at hand. It was necessary to steel myself, steel myself firmly and grit my teeth. In the event that I lost consciousness, I’d given Sasha Artemev a syringe and shown him how to give me an injection. I chose a position half sitting. I explained to Zinovy Teplinsky how to hold the mirror. My poor assistants! At the last minute I looked over at them: they stood there in their surgical whites, whiter than white themselves. I was scared too. But when I picked up the needle with the novocaine and gave myself the first injection, somehow I automatically switched into operating mode, and from that point on I didn’t notice anything else.
“I worked without gloves. It was hard to see. The mirror helps, but it also hinders—after all, it’s showing things backwards. I work mainly by touch. The bleeding is quite heavy, but I take my time—I try to work surely. Opening the peritoneum, I injured the blind gut and had to sew it up. Suddenly it flashed through my mind: there are more injuries here and I didn’t notice them . . . I grow weaker and weaker, my head starts to spin. Every 4-5 minutes I rest for 20-25 seconds. Finally, here it is, the cursed appendage! With horror I notice the dark stain at its base. That means just a day longer and it would have burst and . . .
“At the worst moment of removing the appendix I flagged: my heart seized up and noticeably slowed; my hands felt like rubber. Well, I thought, it’s going to end badly. And all that was left was removing the appendix . . .
“And then I realised that, basically, I was already saved.”
There are a couple of pictures in the link, too.
More on the US bank tax
Further to my last post, Greg Mankiw — who is not a man to lightly advocate an increase in taxes on anything, but who understands very well the problems of negative externalities and implicit guarantees — has written a good post on the matter:
One thing we have learned over the past couple years is that Washington is not going to let large financial institutions fail. The bailouts of the past will surely lead people to expect bailouts in the future. Bailouts are a specific type of subsidy–a contingent subsidy, but a subsidy nonetheless.
In the presence of a government subsidy, firms tend to over-expand beyond the point of economic efficiency. In particular, the expectation of a bailout when things go wrong will lead large financial institutions to grow too much and take on too much risk.
[…]
What to do? We could promise never to bail out financial institutions again. Yet nobody would ever believe us. And when the next financial crisis hits, our past promises would not deter us from doing what seemed expedient at the time.Alternatively, we can offset the effects of the subsidy with a tax. If well written, the new tax law would counteract the effects of the implicit subsidies from expected future bailouts.
My desire for a convex (i.e. increasing marginal rate of) tax derives from the fact that the larger financial institutions are on the receiving end of larger implicit guarantees, even after taking their size into account.
Update: Megan McArdle writes, entirely sensibly (emphasis mine):
That implicit guarantee is very valuable, and the taxpayer should get something in return. But more important is making sure that the federal government is prepared for the possibility that we may have to make good on those guarantees. If we’re going to levy a special tax on TBTF banks, let it be a stiff one, and let it fund a really sizeable insurance pool that can be tapped in emergencies. Like the FDIC, the existance of such a pool would make runs less likely in the shadow banking system, but it would also protect taxpayers. Otherwise, with our mounting entitlement liabilities, we run the risk of offering guarantees we can’t really make good on.
I agree with the idea, but — unlike Megan — I would allow some of it to be collected directly as a tax now on the basis that the initial drawing-down of the pool came before any of the levies were collected (frustration at the political diversion of TARP funds to pay for the Detroit bailout aside).
The US bank tax
Via Felix Salmon, I see the basic idea for the US bank tax has emerged:
The official declined to name the firms that would be subject to the tax aside from A.I.G. But the 50-odd firms, which include 10 to 15 American subsidiaries of foreign institutions, would include Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, General Electric’s GE Capital unit, HSBC, Deutsche Bank, Morgan Stanley, Citigroup and Bank of America.
The tax, which would be collected by the Internal Revenue Service, would amount to about $1.5 million for every $1 billion in bank assets subject to the fee.
According to the official, the taxable assets would exclude what is known as a bank’s tier one capital — its core finances, which include common and preferred stock, disclosed reserves and retained earnings. The tax also would not apply to a bank’s insured deposits from savers, for which banks already pay a fee to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
i.e. 0.15%. It’s certainly simple and that counts for a lot. It’s difficult to argue against something like this.
I would still have liked to see it as a convex function so that, for example, it might be 0.1% for the first 50 billion of qualifying assets, 0.2% for the next 50 billion and 0.3% thereafter.
Better yet, pick a size that represents too big to fail (yes, it would be somewhat arbitrary), then set it at 0% below, and increasing convexly above, that limit.
Avatar
The visual detail is incredible. It is a must-see in 3D. It was designed for 3D.
The broad plot ideas are nothing special, particularly if you’ve read much sci fi or fantasy, but that’s okay. The moral theme (humans in general and corporations in particular are evil, tree hugging Gaia worship is cool) is rammed down your throat too much — I would have liked to see something a little more Alien-and-The-Abyss-meet-your-classic-dragon-fantasy-novel and a little less Princess-Mononoke-and-Pocahontas-read-the-Green-Left-Weekly — but, as my brother points out, it’s not a film written for me, but for it’s target audience, who apparantly like broad brush strokes and simplistic themes.
Even so, I would have liked some proper character development and better acting. The bad guy is cartoonish. The corporate stooge is simpering and never displays any of the internal conflict the role clearly calls for. This standard of visual detail will soon enough be the new normal and once that happens, nobody will remember Avatar, which is a shame.
Mike Russell has written a review that I generally agree with, here (lots of spoilers).
Becoming British
I’ll never try to pretend that a Scottish tennis player or a bunch of South African cricket players are English, but today I sent off my application for naturalisation as a British citizen. My grandmother would be proud.